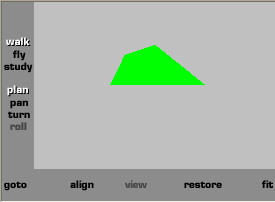
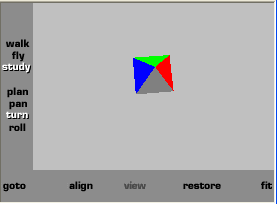
|
Shape
{
geometry IndexedFaceSet {
coord Coordinate {
point [
1 0 1, 1 0 -1, -1 0 -1, -1 0 1, 0 1.5 0
]
}
coordIndex [
0 1 2 3 -1,
0 1 4 -1,
1 2 4 -1,
2 3 4 -1,
3 0 4
]
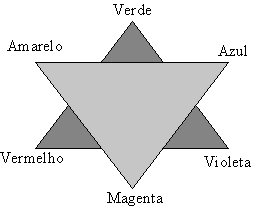
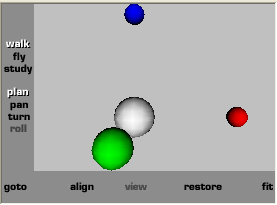
color Color { # definição de 5
cores
color[1 0 1, 1 0 0, 0 1 0, 0 0 1, .5 .5 .5]
}
colorIndex [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
# lê-se: coloque cor [0] na face[0]; cor [1] na face[1] etc;
colorPerVertex FALSE
#se false: implica cor/face
solid FALSE #fundo invisivel
}
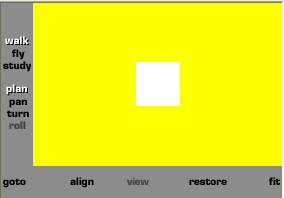
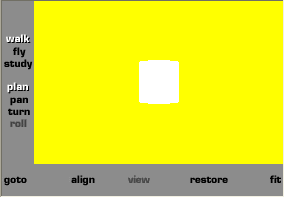
} # Girar a
imagem para melhor visualizar
# Como
execício: coloque na face[0] magenta; na face[1] preta;
#
na face[2] amarelo; na face[3] branca e na face[4] ciano
|